Authorization use cases
TransAPI requires authorization for all processed requests. TransAPI authorization is based on OAuth 2.0 authorization framework.
In order to send authorized request, first you need to obtain an access token.
Access token encapsulates the identity of a user and his granted permissions.
Based on the access token TransAPI decides whether user has permission to access requested data or not.
Trans Authorization Server supports OAuth 2 flows you can use to obtain an access token:
- 2-legged flow
- 3-legged flow
You can determine which of them is most suitable for your application basing on it's type.
| Application type | Flow |
|---|---|
| Public system | 3-legged |
| TMS | 3-legged |
| ERP | 2-legged |
| CRM | 2-legged |
Supported OAuth authorization flows
Prerequisites
In order to start using TransAPI, you need to register your application.
After that you will receive a unique client_id and client_secret keys to use in the authorization process.
3-legged flow use case
In this flow 3 parties (legs) are involved:
- client - an application registered in TransAPI
- server - Trans Authorization Server and it's OAuth endpoints
- resource owner - a user of an application registered in TransAPI
This use case will show you how to:
- ask user to grant your application permissions to access loads offers
- how to get these loads offers
Note, that this use case uses example data, that should be changed when using TransAPI.
Application requests authorization
The 3-legged authorization starts with an application sending a request to
/oauth2/authorizeendpoint.In this case it's necessary to ask user (resource owner) for privileges to manage his offers. This in particular requires access to
offers.loads.managescope.GET /oauth2/authorize?client_id=example_app_client_id &response_type=code &redirect_uri=https%3a%2f%2fexample.com%2fapplicationendpoint &scope=offers.loads.manage HTTP/1.1 Host: auth.system.trans.euUser is inquired to authorize application to access data within requested scope.
If the user is not currently signed in, login form will be presented by the Trans Authorization Server where user can sign in using Trans.eu credentials.

After signing in Trans Authorization Server displays page with list of scopes with details and asks user to grant application permissions to the listed scopes.
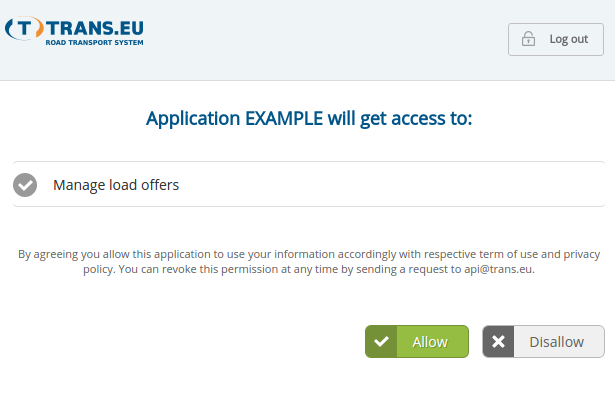
User grants access to requested scope and is redirected back to specified redirect URI
After the user has granted requested access to the application, he's redirected to URI address provided in
redirect_uriparameter of authorization request. Response query string containscodeparameter, which is added to theredirect_uriduring redirection.For example:
HTTP/1.1 302 Found Location: https://example.com/applicationpoint?code=a1c94032558c6d0ba98b998299a63135bce063b1Application exchanges the authorization code for an access token
After the authorization code has been received, the application needs to exchange it for an access token by making another request to the
/oauth2/tokenendpoint.POST /oauth2/token Host: auth.system.trans.eu Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded grant_type=authorization_code &code=a1c94032558c6d0ba98b998299a63135bce063b1 &redirect_uri=https%3a%2f%2fexample.com%2fapplicationendpoint &client_id=example_app_client_id &client_secret=example_app_secretThe access token is returned to application
When the response of previous request has status code
200 OK, in the response body there will be following JSON data:{ "access_token": "d8f82913743d3fad75e382da0750d1988fb76a9d", "expires_in": 3600, "token_type": "Bearer", "scope": "offers.loads.manage", "refresh_token": "442341616db6a8a459051b8c3f9a957edadeeb97" }Use the access token to access the user loads data.
Having the access token application can fetch user loads by including access token in header.
GET /api/rest/v1/loads Host: offers.system.trans.eu Authorization: Bearer 59d9aa9b15cd59a61fc52014792efb6caa82373b Accept: application/hal+json
2-legged flow use case
In this flow 2 parties (legs) are involved:
- client - in this case client is resource owner at the same time, but it is still an application registered in TransAPI
- server - this is the Trans Authorization Server and it's OAuth endpoints
In 2-legged authorization user signs in application using his Trans credentials.
Then, those credentials can be used to obtain access token.
This section will show you how to:
- obtain access token without user interaction,
- access loads offers of user,
Application requests an access token
POST /oauth2/token Host: auth.system.trans.eu Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded grant_type=password &username=jan.kowalski@trans.eu &password=abc123 &client_id=example_app_client_id &client_secret=example_app_secret &scope=offers.loads.manageOn success, the response has status code 200 OK and following JSON data in response body:
{ "access_token": "d8f82913743d3fad75e382da0750d1988fb76a9d", "expires_in": 3600, "token_type": "Bearer", "scope": "offers.loads.manage", "refresh_token": "442341616db6a8a459051b8c3f9a957edadeeb97" }Use the access token to access the user loads data.
Example:
GET /api/rest/v1/loads Host: offers.system.trans.eu Authorization: Bearer d8f82913743d3fad75e382da0750d1988fb76a9d Accept: application/hal+json
